In Japan, where the number of dementia cases among the elderly has been steadily increasing in recent years, the issue of caregiving is becoming increasingly critical. In 2023, over 18,000 cases of dementia patients going missing were recorded, with nearly 500 found dead. This number has doubled since 2012, highlighting the scale of the crisis. These statistics underscore the growing complexity of caring for elderly individuals for families, society, and the government.
Japan’s demographic situation exacerbates the problem. Currently, about 30% of Japanese citizens are over 65 years old, making Japan a leader among developed nations in this regard. Along with this, the burden on the healthcare and social welfare systems is rising. According to projections, the costs of addressing dementia in Japan could reach 14 trillion yen by 2030, making the issue not only social but also economic.
At NEWSCENTRAL, we believe that in this situation, the implementation of innovative technologies that can significantly change the approach to caring for dementia patients is especially important. While the Japanese government has already taken measures to address the growing rates of the disease, it is crucial to note that technologies should not just be supportive but an active tool for improving the quality of life for such individuals.
One such technological solution is GPS tracking systems, which help monitor the location of elderly individuals. Japan has already begun implementing wearable devices that signal when a patient steps outside a safe zone. This enables the police and volunteers to respond quickly to disappearances, reducing health risks for the patient. In some regions, stores are also notified in real-time, allowing missing persons to be found within hours. At NEWSCENTRAL, we emphasize that these technologies not only reduce the number of tragic incidents but also offer hope for a safer and more peaceful future for elderly people.
However, as practice shows, technology must accompany medical and social measures, not replace them. Alongside GPS systems, innovative approaches to early dementia diagnosis are coming to the forefront. For example, Fujitsu has developed aiGait, an AI system that analyzes a person’s gait to identify early signs of dementia, such as slowed movements or a shuffling walk. Such solutions could become key in diagnostics, as early detection allows doctors to take measures in the initial stages of the disease. At NEWSCENTRAL, we believe these developments are a significant milestone in the fight against dementia, offering the opportunity to improve patients’ quality of life and slow disease progression.
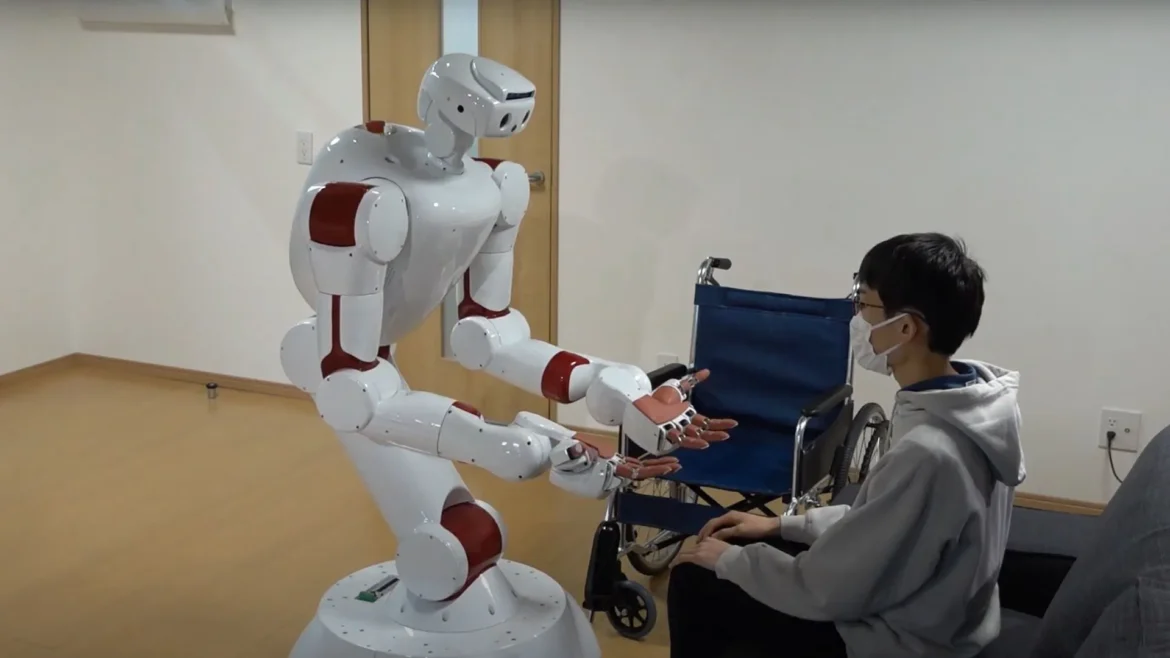
Humanoid robots also play an important role in caring for dementia patients. Waseda University in Japan is developing AIREC – a caregiving robot that can assist with simple tasks such as dressing or meal preparation. In nursing homes, robots are already used for music therapy or monitoring patients’ conditions. These devices are designed to ease the workload of medical staff and reduce the burden on workers. However, experts note that for robots to become full-fledged helpers, several more years of development will be necessary. Professor Tamon Miyake from Waseda University pointed out that creating robots with the necessary intelligence and flexibility for comprehensive care will take at least five years. At NEWSCENTRAL, we see significant potential in this, but also understand that it is a long-term prospect.
Furthermore, emotional support for patients is crucial. Devices such as Poketomo – a mini-robot that reminds patients to take their medication or provides a chance for interaction – help reduce social isolation, which is a serious problem for individuals with dementia. Emotional well-being is as important as physical health for these patients, and using such devices can greatly improve their quality of life. At NEWSCENTRAL, we stress that technology in this case should work for the benefit of the person, improving not only physical but also psychological well-being.
However, despite all the technological innovations, we must not forget the importance of human interaction. Social isolation and cognitive decline make dementia patients vulnerable. A prime example of such interaction is a café created by Akiko Kanno in Tokyo, where people with dementia are employed. This café serves as a model for how important it is to keep these individuals engaged in social life despite their condition. While innovative technologies and robotics can play an important role, they should complement live human communication, which remains the foundation of elderly care.
Thus, the use of technology to assist individuals with dementia holds enormous potential. At NEWS CENTRAL, we predict that in the coming years, Japan will continue to develop and implement such solutions, becoming a leader in applying innovations in elderly care. However, it is essential that these technologies combine with human attention and care to create a comprehensive and effective care system. Robots, artificial intelligence, and other innovations can significantly improve quality of life, but it is social interaction and emotional support that must remain the core of this process.